When it comes to handling zip files, Windows users have always had the
advantage with WinRAR that automatically helps to extract and
compressing zip files. On the other hand, in case of Linux operating
systems, users have to either download other compatible tools or perform
the operation through command terminal.
What is a .RAR File Extension?
For users who don’t know, a RAR file is a compressed file that is
split into a set of multi-volume files. This is usually done in cases
where there are large file sets that are needed to be shared or
transferred, hence are compressed into a zip file. Similarly, for zip
files, when they are transferred or downloaded from the internet need to
be extracted. A number of tools are available to help extract and
compress these files within seconds, regardless of their size or
quantity.
Extracting RAR Files in Linux distributions
RAR is a free tool that is pre-installed on Windows operating systems
but unfortunately doesn’t support Linux platforms. If you will try
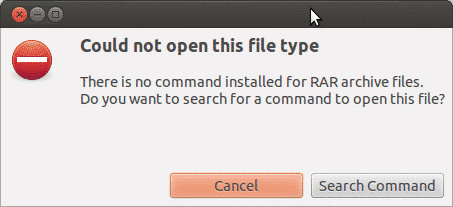
extracting in Ubuntu, the archive manager will show you the following
dialogue box:
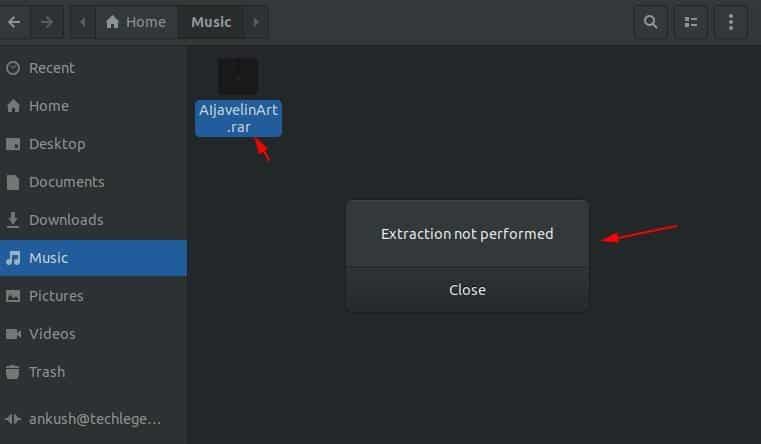
This is because the system won’t recognize the file type like Windows
and does not have any supported tool to extract it. In other cases, it
will also display an error somewhat like this:
Read on below to find out how you can install RAR tools on Linux and use those to open, extract, and compress a file.
How to Install Unrar tool in Linux
Unrar is compatible mostly for Linux distributions where you can easily install the package from the command terminal using the apt programs.
Open Command Terminal and type the following command(s) if you’re using Ubuntu or Debian based distros:
$ sudo apt-get install unrar
Or
$ sudo apt install unrar
If you are using Fedora distro, type the command in your command prompt:
$ sudp dnf install unrar
For users using CentOS/ RHEL 64-bit distros, you can install the Unrar tool using these commands:
$ cd /tmp
$ wget https://www.rarlab.com/rar/rarlinux-x64- tar.gz
$ tar –zxvf rarlinux-x64-tar.gz
$ cd rar
$ sudo cp –v rar unrar /usr/local/bin/
(Just remove ‘x64’ from the above command if you want to alter it for 32-bit systems)
How to Extract a RAR File in Linux
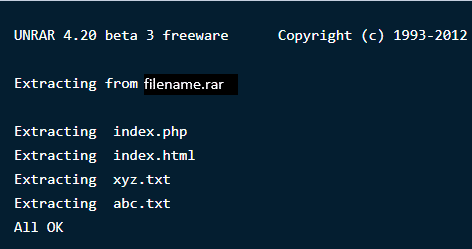
To open or extract a .rar extension file in your current working directory, type the following command in the terminal:
$ unrar e filename.rar
This will start extracting your file using the Unrar tool like this below:
Note: Since you have the Unrar tool, you can also perform these
operations directly through the right click, besides using these
commands on the terminal.
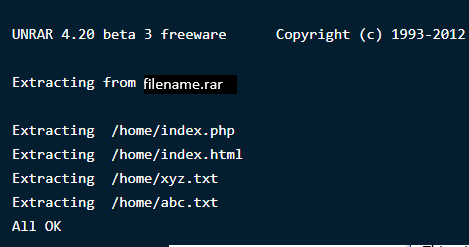
To open or extract a .rar extension file in any specific path or
directory, type the following command in the terminal. This will extract
the files and locate them in the specified directory.
$ unrar e filename.rar /home/
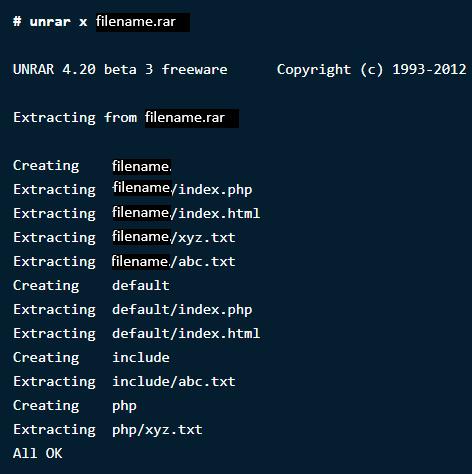
If you want to open or extract a .rar extension file in their original directory, use the following command:
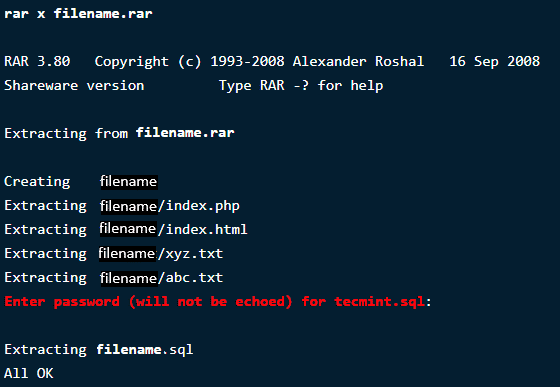
$ unrar x filename.rar
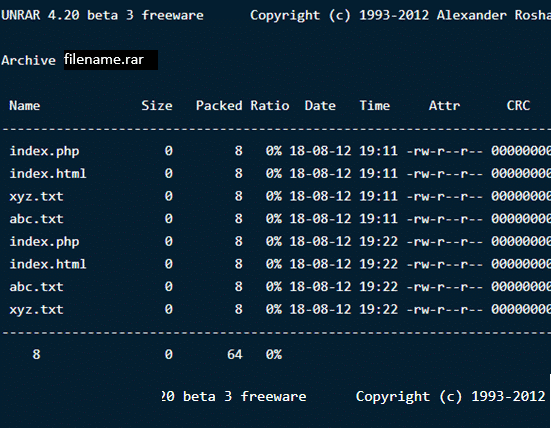
How to View Contents inside a RAR File in Linux
A compressed file contains multiple files of large sizes that are
zipped together inside it. If you want to list out all the file contents
inside an archive file, use the command below. This will display a list
of files with their name, size, time, date created and permissions.
$ unrar l filename.rar
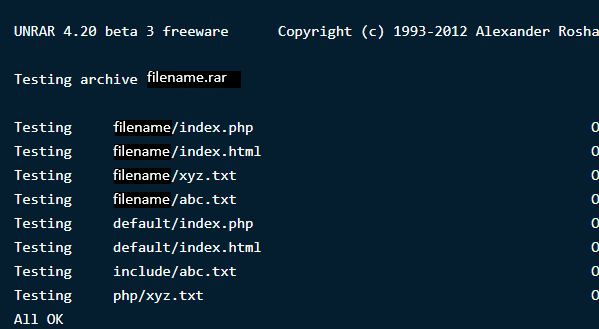
Testing a RAR File in Linux
If for instance, you have downloaded a file from the internet and
would like to test its integrity, the Unrar tools offers that too. The
following command will do a complete check on the archive file and its
contents, and then show the results. Type:
$ unrar t filename.rar
The unrar tool that we just downloaded uses the unrar command
to carry out the above tasks. It lets you extract, list out and test
files. There is no option for creating a rar file with this particular
tool. Therefore, we will install another Linux command-line utility
called RAR to create compressed/archive files.
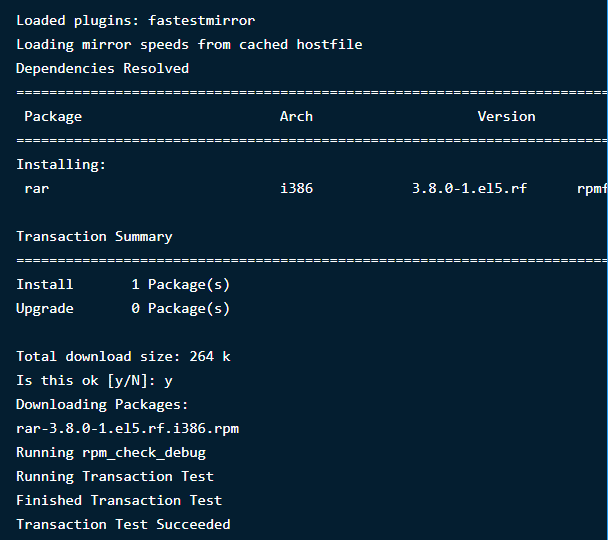
Installing RAR in Linux
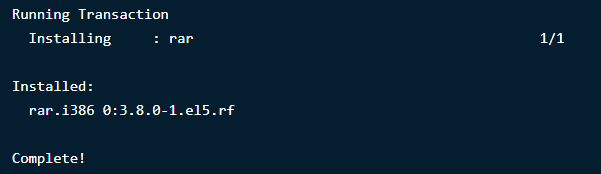
To install the RAR command option, type the following commands in the terminal:
$ sudo apt-get install rar
$ sudo dnf install rar
$ yum install rar
After you execute the commands, the result will be:
Creating RAR Files in Linux
In order to create a .rar file in Linux distribution, you will need to run the following command:
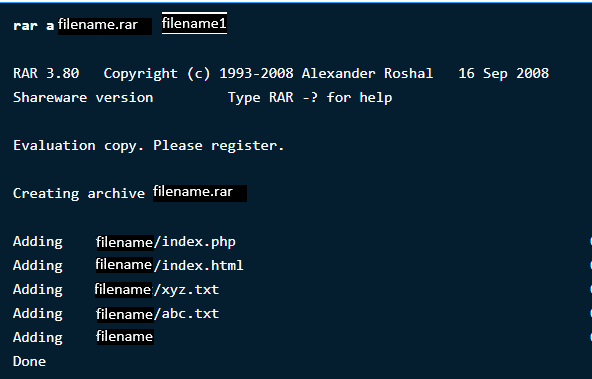
$ rar a filename.rar filename1
This will create an archive file name ‘filename’ for the directory filename1. See how this will look like below:
Deleting Files from any Archive
Out of the multiple files in an archive, if you want to delete a
particular file through the command terminal, type the following
command:
$ rar d filename.rar
Recovering deleted Archives
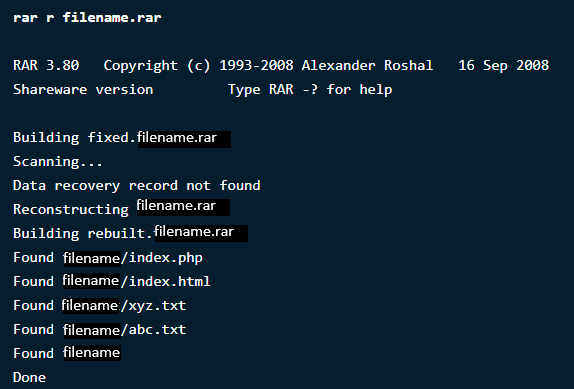
If you deleted an archive file by accident or lost it through data
loss, don’t worry, you can always recover it back. The following command
will recover the file back or will fix it if there has been any loss or
damage.
$ rar r filename.rar
Setting password on a Particular Archive
This incredible Rar tool lets you do a number of interesting things
with your archive files from creating, deleting, and adding, to changing
their directories and protecting them through passwords.
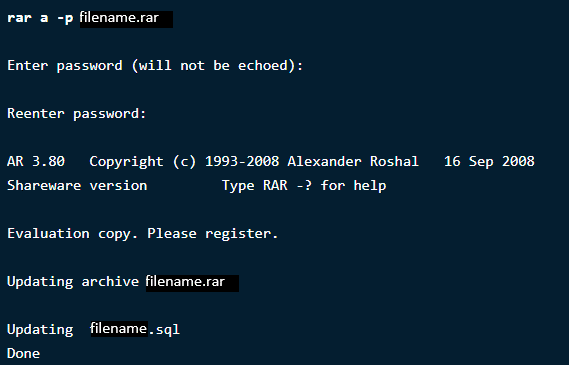
If you want to protect your files from unknown access or extraction,
you can set a password on them. To password-protect your file, type the
following command:
$ rar a –p filename.rar
Now, to verify the changes, type the command to open the directory to see if it asks for password.
Wrap Up
RAR and UNRAR are very useful when it comes to handling and managing
files in Linux. They provide multiple options to make your work easier
and more convenient. When compared to Windows, things get a little
complicated for Ubuntu, but these commands are simple, easy to execute
and give results within seconds.
If you need more description on the commands, just the run the following two:
$ man unrar
$ man rar
$ man rar
Comments
Post a Comment